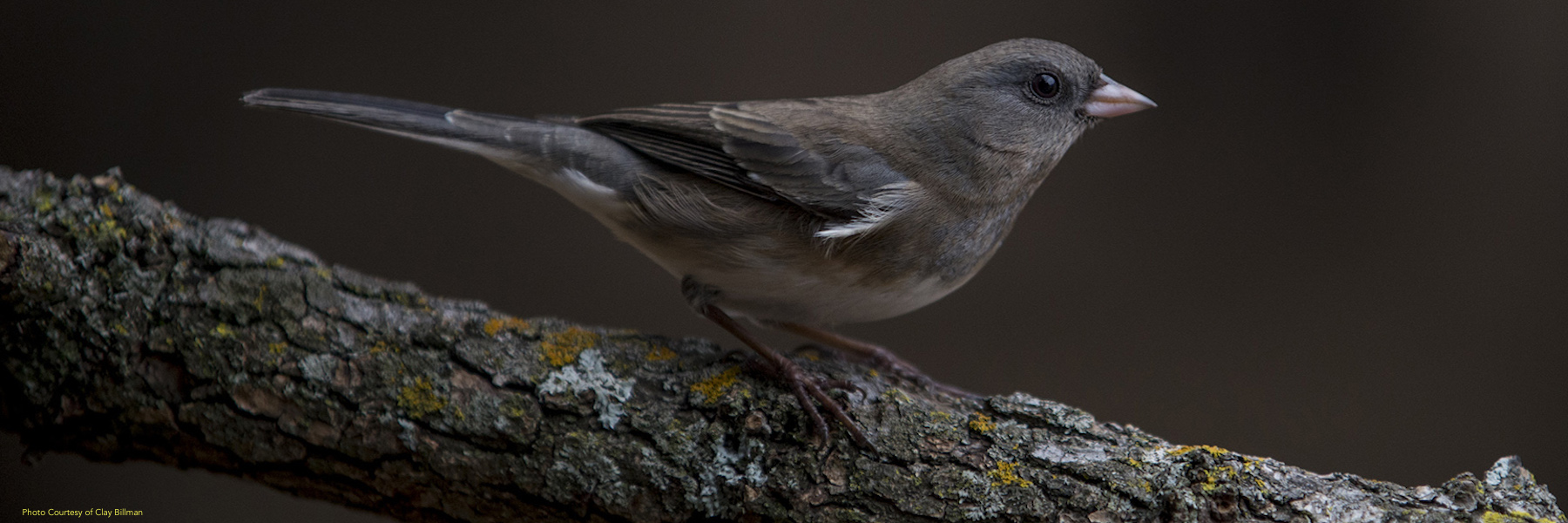
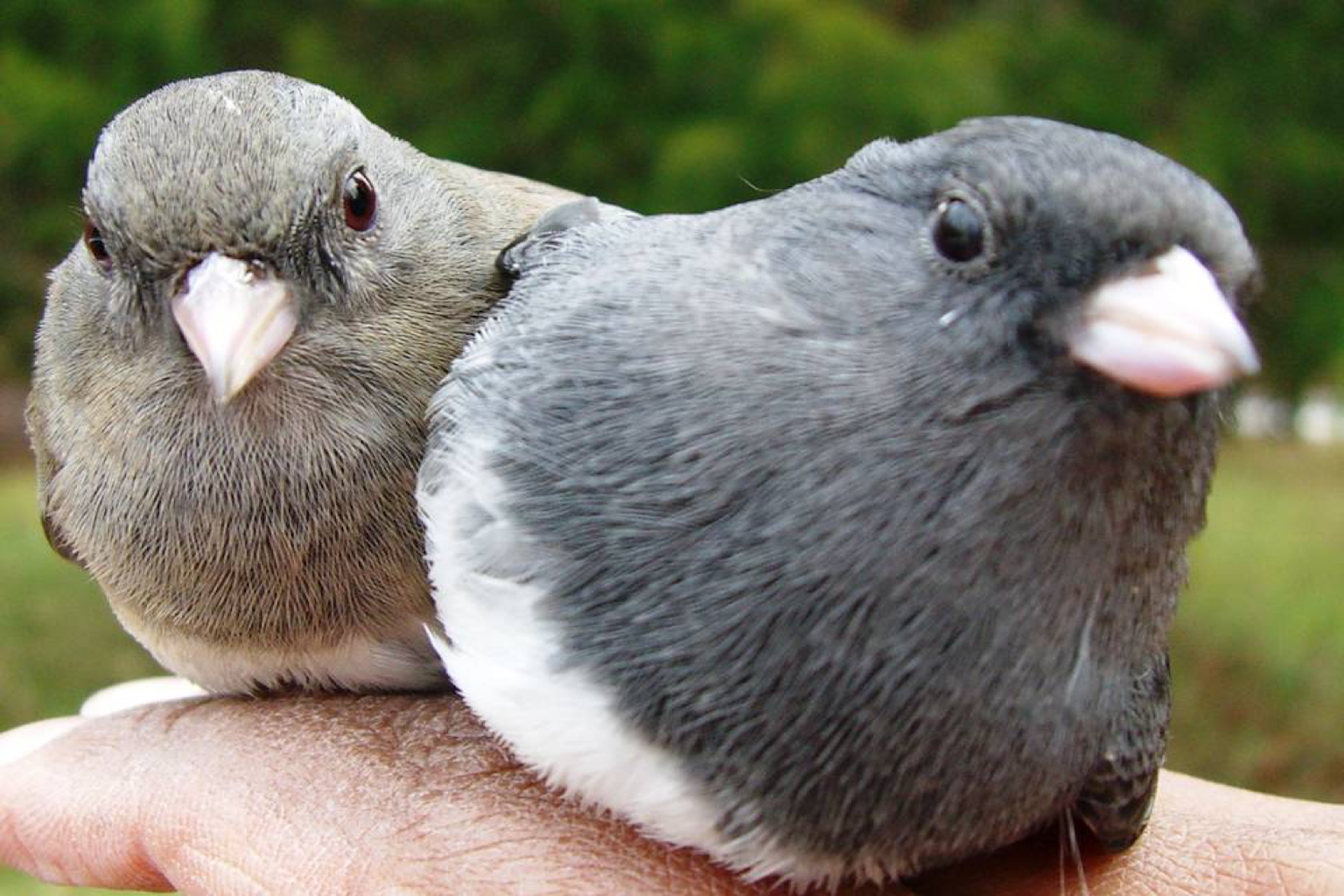
The Mountain Lake Biological Station in southwestern Virginia has a long association with the Ketterson Lab. Since 1983, Ketterson lab members have been studying the population of slate-colored juncos (Junco hyemalis carolinensis) that breed in the high-elevation Appalachian forest at and around the station. Over the years, we've accumulated information on over 14,000 individually-marked juncos and more than 3,000 nesting attempts.